|
|
|||
| NRAO Home > CASA > CASA Cookbook and User Reference Manual |
|
||
5.3.18 Wide-field imaging and deconvolution in clean
When imaging sufficiently large angular regions, the sky can no longer be treated as a two-dimensional plane and the use of the standard clean task will produce distortions around sources that become increasingly severe with increasing distance from the phase center. In this case, one must use a “wide-field” imaging algorithm such as w-projection or faceting.
When is wide-field imaging needed? The number of required facets N depends on the the maximum baseline Bmax, the dish diameter D and the wavelength λ as:
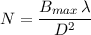 | (5.13) |
and w-projection is required when N > 1. (For details, see “Synthesis Imaging in Radio Astronomy II”, ed. Taylor, G., Carilli, C., Perley, R. 1999). With 25 m diameter JVLA dishes (which implies that imaging is requested out to the primary beam FWHM), w-projection is required for array configurations as listed in Table 5.1.
| Receiver Band | Wavelength [cm] | Array configurations |
| 4 | 430 | A/B/C/D |
| L | 20 | A/B/C |
| S | 10 | A/B |
| C | 5 | A |
| X | 3 | A |
| Ku | 2 | A |
| K | 1.4 | – |
| Ka | 0.9 | – |
| Q | 0.7 | – |
The relevant inputs for clean for wide-field imaging are:
wprojplanes = 1 # Number of w-projection planes for convolution
facets = 1 # Number of facets along each axis (main image only)
Most of the clean parameters behave as described previously.
Wide-field imaging can be carried out using two major modes: First, the w-projection mode as chosen with ftmachine deals with the w-term (the phase associated with the sky/array curvature) internally. Secondly, the image can be broken into many facets, each small enough so that the w-term is not significant. These two basic methods can be combined, as discussed below in § 5.3.18.4.
5.3.18.2 Setting up w-projection
5.3.18.3 Setting up faceting
5.3.18.4 Combination of w-projection and faceting
More information about CASA may be found at the
CASA web page
Copyright © 2010 Associated Universities Inc., Washington, D.C.
This code is available under the terms of the GNU General Public Lincense
Home |
Contact Us |
Directories |
Site Map |
Help |
Privacy Policy |
Search
