|
|
|||
| NRAO Home > CASA > CASA Cookbook and User Reference Manual |
|
||
4.2.2 Keeping Track of Calibration Tables
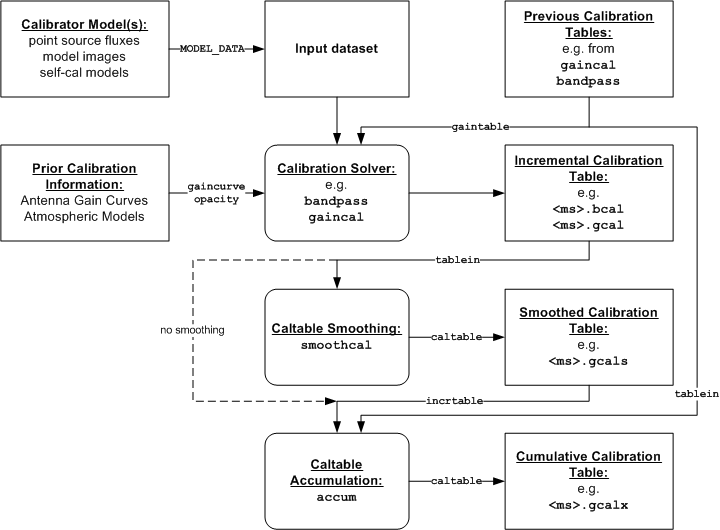
_________________________________________________________________________________________
The calibration tables are the currency that is exchanged between the calibration tasks. The “solver” tasks (gaincal, bandpass, blcal, polcal) take in the MS (which may have a calibration model attached) and previous calibration tables, and will output an “incremental” calibration table (it increments the previous calibration, if any). This table can then be smoothed using smoothcal if desired.
You can optionally accumulate the incremental calibration onto previous calibration tables with accum, which will then output a cumulative calibration table. This task will also interpolate onto a different time scale. See § 4.5.5 for more on accumulation and interpolation.
Figure 4.2 graphs the flow of these tables through the sequence
Note that this sequence applied to separate types of tables (e.g. ’B’, ’G’) although tables of other types can be previous calibration input to the solver.
The final set of cumulative calibration tables is what is applied to the data using applycal. You will have to keep track of which tables are the intermediate incremental tables, and which are cumulative, and which were previous to certain steps so that they can also be previous to later steps until accumulation. This can be a confusing business, and it will help if you adopt a consistent table naming scheme (see Figure 4.2) for an example naming scheme).
More information about CASA may be found at the
CASA web page
Copyright © 2010 Associated Universities Inc., Washington, D.C.
This code is available under the terms of the GNU General Public Lincense
Home |
Contact Us |
Directories |
Site Map |
Help |
Privacy Policy |
Search
