|
|
|||
| NRAO Home > CASA > CASA Cookbook and User Reference Manual |
|
||
4.5.5.1 Interpolation using (accum)
Calibration solutions (most notably G or T) can be interpolated onto the timestamps of the science target observations using accum.
The following example uses accum to interpolate an existing table onto a new time grid:
tablein=’’,
accumtime=20.0,
incrtable=’n4826_16apr.gcal’,
caltable=’n4826_16apr.20s.gcal’,
interp=’linear’,
spwmap=[0,1,1,1,1,1])
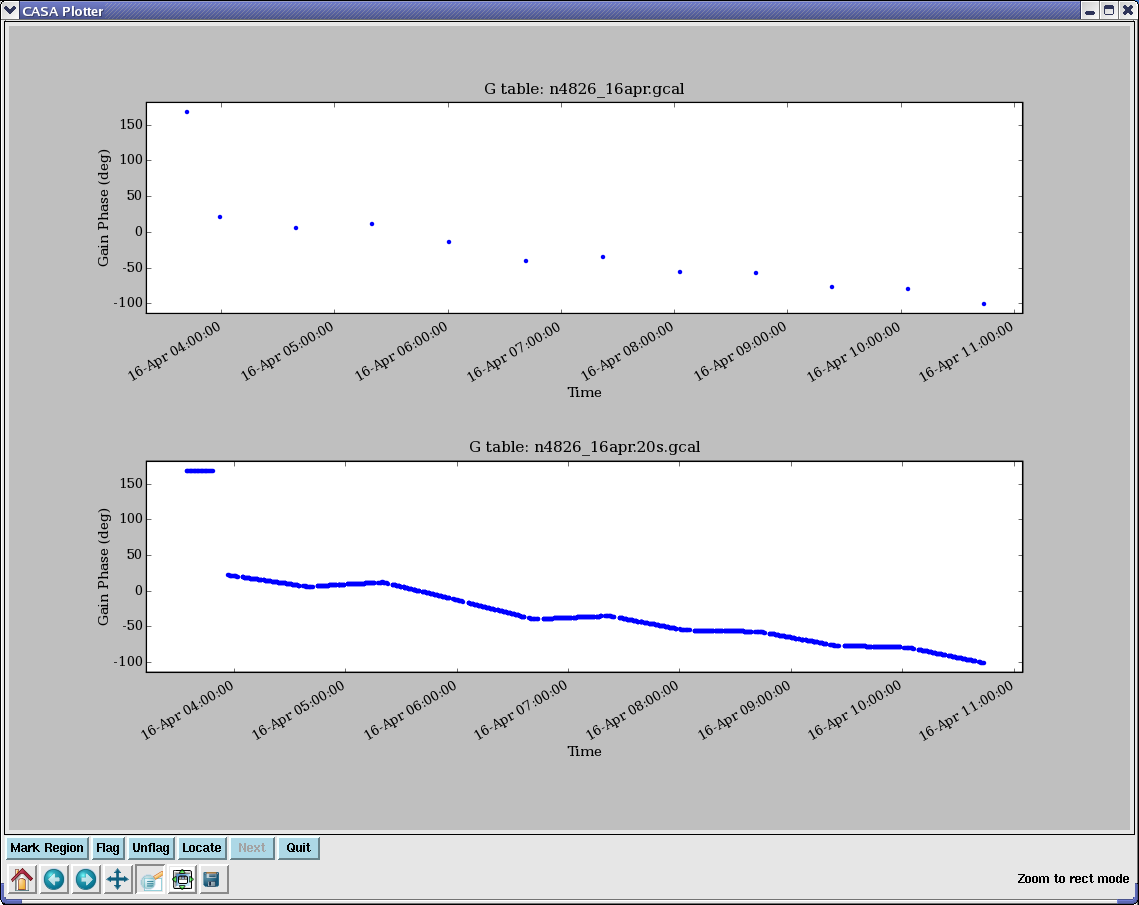
plotcal(’n4826_16apr.gcal’,’’,’phase’,antenna=’1’,subplot=211)
plotcal(’n4826_16apr.20s.gcal’,’’,’phase’,antenna=’1’,subplot=212)
See Figure 4.9 for the plotcal results. The data used in this example is BIMA data (single polarization YY) where the calibrators were observed in single continuum spectral windows (spw=’0,1’) and the target NGC4826 was observed in 64-channel line windows (spw=’2,3,4,5’). Thus, it is necessary to use spwmap=[0,1,1,1,1,1] to map the bandpass calibrator in spw=’0’ onto itself, and the phase calibrator in spw=’1’ onto the target source in spw=’2,3,4,5’.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
More information about CASA may be found at the
CASA web page
Copyright © 2010 Associated Universities Inc., Washington, D.C.
This code is available under the terms of the GNU General Public Lincense
Home |
Contact Us |
Directories |
Site Map |
Help |
Privacy Policy |
Search
