
 News
News
| Getting Started | Documentation | Glish | Learn More | Programming | Contact Us |

| Version 1.9 Build 000 |
 News
News
|
Table
taper function
Tcl/Tk
TCP/IP
telescope
temperature
tertiary
TeX
tied array
TIFF
time
time-average smearing
time-baseline order
time standard
tipping scan
Tool
Tool Manager
total power receiver
transfer function
tropical year
troposphere
turret
In AIPS++, a Table consists of a header, and a main data table. The main data table consists of a number of rows and columns. A value is stored at the intersection of each row and column. All values in a column must be of the same type. The header consists of sets of keywords: one set for the whole Table, and (potentially) one set per column.
See grading function (single antenna), u-v taper function (interferometry).
A software system providing a simple command language (TCL), and a set of widgets for use in building GUIs. Tcl/Tk is a popular system and has many adherents. The Tk widgets are bound to Glish and are used for GUIs in AIPS++.
An acronym for Transmission Control Protocol over Internet Protocol; the de facto standard Ethernet protocols incorporated into 4.2BSD Unix. TCP/IP was developed by DARPA for inter-networking, encompassing both network layer and transport layer protocols. While TCP and IP specify two protocols at specific layers, TCP/IP is often used to refer to the entire protocol suite based upon these, including telnet, FTP, UDP and RDP.
In radio astronomy, a term that may be used to mean either
The sense is usually apparent from the context.
In radio astronomy, many normalized measures of spectral power density are referred to as temperatures. See antenna temperature, brightness temperature, system temperature.
Adjective identifying the third surface to reflect radiation in a telescope.
In a radio telescope, the primary reflector is usually the surface of the panels or, in a low-frequency antenna, a wire mesh. This is sometimes referred to as the main reflector or simply, the dish. The secondary reflector, if any, is often called the subreflector. While smaller than the primary reflector, it is often large relative to a person. By contrast, any tertiary reflector is usually a small device used only at high radio frequencies and which is often therefore described as a "mirror", by analogy with optical systems.
A powerful macro-based text formatter written by Donald Knuth, popular in the scientific community. Knuth began work on TeX because of problems he experienced with traditional typesetting in volumes I--III of his monumental Art of Computer Programming. The language was effectively frozen in 1985. Well-known extensions to TeX include:
TeX can be obtained from the labrea.stanford.edu archive at Stanford University.
Tagged Image File Format: a file format used for still-image bitmaps, stored in tagged fields. Application programs can use the tags to accept or ignore fields, depending on their capabilities.
A term used to describe a VLBI observing mode at the WSRT wherein all antennas are autocorrelated to obtain a large collecting area without high spatial resolution. See phased array.
Many different time systems are relevant in astronomy. See atomic time, local sidereal time, sidereal day, Universal Time, UTC. For a quick summary, see the U.S. Naval Observatory's Systems of Time WWW page at http://tycho.usno.navy.mil/systime.html.
In a radio interferometer image, the space-variant broadening
of the point spread function
(or beam) which is due to time averaging of
the u-v data. When, for example, the visibility data along a
u-v track are averaged, with equal weight, over time
intervals of width 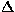 t
sec., the visibility amplitude of a point source is reduced by a factor
t
sec., the visibility amplitude of a point source is reduced by a factor
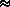 sinc
sinc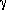 , where
, where 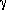

 (u'x + v'y +
w'z)
(u'x + v'y +
w'z)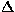 t,
where the primes denote the time rate of change of the spatial frequency
coordinates (u,v,w) along the track (wavelengths/sec.), and
where (x,y,z) denotes the direction cosines of the location
of the point source with respect to the
phase tracking center.
Compare bandwidth smearing.
t,
where the primes denote the time rate of change of the spatial frequency
coordinates (u,v,w) along the track (wavelengths/sec.), and
where (x,y,z) denotes the direction cosines of the location
of the point source with respect to the
phase tracking center.
Compare bandwidth smearing.
A set of visibility measurements is said to be in time-baseline
order if the ordering is such that all of the data obtained at time
t , sorted into the
canonical ordering by baseline, occur first, followed by the data
obtained at time t
, sorted into the
canonical ordering by baseline, occur first, followed by the data
obtained at time t , again ordered
canonically, etc., etc. (The canonical ordering by baseline is the order
[1,2], [1,3], ..... [1,n], [2,3], ...... [(n-1),n].) Compare baseline-time order.
, again ordered
canonically, etc., etc. (The canonical ordering by baseline is the order
[1,2], [1,3], ..... [1,n], [2,3], ...... [(n-1),n].) Compare baseline-time order.
Time-baseline ordering of a u-v database is convenient for calibration purposes.
A high-stability oscillator used for keeping accurate time. When based on atomic transitions, also known as an atomic clock. The most common such devices are the cesium-beam-tube resonator, the rubidium-gas-cell resonator and the atomic hydrogen maser.
A mode of observing in radio astronomy wherein the system temperature of a receiver on an antenna is measured while the antenna is moved (scanned) in zenith angle. By using a synchronous detector to measure the difference between the system temperatures with the receiver connected to a feed looking at the sky and to a constant-temperature load, one may use a tipping scan to infer the zenith optical depth of the atmosphere at the time and frequency of the measurements. Tipping scans are therefore used to monitor atmospheric attenuation.
In AIPS++, a tool is a collection of Glish functions that can be applied to some common data, such as a MeasurementSet or Image. A tool must be created for a specific data set using a constructor and then the associated functions can applied to that data. A tool can also be considered to be an object, and the tool functions can be considered to be the object methods. An tool is implemented as a Glish closure object and thus usually consists of a Glish record containing functions.
The tool manager allows construction, destruction, and interaction with AIPS++ tools and global functions. The AIPS++ tool manager has both graphical and command line user interfaces.
A receiving system (radiometer) that responds to the total power received by the antenna that is connected to it, rather than to the difference between this power and some reference power, i.e. an unswitched receiver. To be useful, total power receivers must be built with special attention to stabilizing their gains by (a) regulating power supplies, (b) controlling ambient temperatures, (c) ensuring mechanical rigidity of all components and connections, and (d) maintaining a constant local oscillator power in any mixer systems.
A transform which can be used to describe the output of a device (say, an electrical transducer) as a function of the input to the device. In digital imaging, often applied to the function used to transform between intensities in a stored image and those in the representation of that image in the memory of a video display device.
The interval of time between successive passages of the Sun through the vernal equinox (365.2422 mean solar days).
The lowest region of the Earth's atmosphere, from ground level to the tropopause, where the temperature gradient goes to zero (height about 15 km). The troposphere is the region where most weather occurs.
A turntable that is rotated to move a feed and/or front end receiver package to the focus of an antenna, or to move a (usually tertiary) mirror into the optical path of an antenna.
You could now go back to the:
Copyright © 1995,1996,1997,1999,2000 Associated Universities Inc., Washington, D.C.
abridle@nrao.edu, 26 August 1996 11:50 EDT