
| Version 1.9 Build 1367
|
|



Next: References
Up: The Generic Instrument: V Design of Cross-calibration
Previous: Some comments on capabilities available inside AIPS++
Our preferred approach to calibration uses the reference table or MS
concept to keep both the original data together in one MS and to provide
calibrated views of that data via reference tables.
- The MeasurementSet M is subject to some
selection, Scal, to produce a logical subset MS
M(Scal), the
calibrator MS. The selection used is of interest in two ways: first
to ensure that the correction is applied to the relevant data
(e.g. 6cm to 6cm observations), and second as information to the user
(e.g. ``wind-velocity
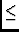 3 m/s'').
3 m/s'').
- For each such calibrator MS, a SkyModel is used to predict the corresponding coherences.
- For each such calibrator MS, one will want to perform a solution
for one or more MeasurementComponents (e.g. GJones and
DJones).
- Each MeasurementComponent is then stored as a Table in the calibrator
MS.
- The MeasurementSet M is subject to some
selection,
Ssource, to produce a logical subset MS
M(Ssource), the
source MS.
- MeasurementComponents are then explicitly copied from calibrator to
source MS, either by the user or by some simple program.
- After copying, a MeasurementComponent can be subject to a number of
operations:
- Re-interpolation in some coordinate such as time or some derived
quantity such as antenna elevation or airmass,
- Editing by hand or by algorithm,
- Boot-strapping of some form (e.g. determination of the flux of
some sources from a primary calibrater),
- Recasting to another form (e.g. antenna-based phases to
position-based phase screen).
All of these are probably best thought of as construction of a new MeasurementComponent that replaces the initial one.
The net result is that one main MS and a number of reference MSes pointing to
it and containing the relevant MeasurementComponents. This scheme
has a number of advantages:
- 1.
- (Relative) simplicity. We consider this to be very important,
- 2.
- The MeasurementComponents in the source MSes exist independently of the
calibrator MSes and can be edited or munged as one chooses,
- 3.
- Self-calibration is easily accomodated by simply updating the
MeasurementComponents in the source MSes.
An alternate but more complicated approach is to defer the connection
between sources and calibrators until the correction of data is
actually performed. In this scheme, each reference MS is assigned a
unique integer, CG, and an MS column ``CALIBRATION_GROUP'' is set to
that integer. The links between calibrator and source are then made
via this index. The data for which these corrections are to be applied
are selected via a selection
Ssource to form a target MS,
M(Ssource). The column CALIBRATION_GROUP of this MS, is set to
CG. We discarded this type of deferred selection of MeasurementComponents as being overly complex, and not allowing the
user to munge the MeasurementComponents ``by hand''.



Next: References
Up: The Generic Instrument: V Design of Cross-calibration
Previous: Some comments on capabilities available inside AIPS++
Contents
Please send questions or comments about AIPS++ to aips2-request@nrao.edu.
Copyright © 1995-2000 Associated Universities Inc.,
Washington, D.C.
Return to AIPS++ Home Page
2006-03-28

 News
News  FAQ
FAQ
 Search
Search
 Home
Home
