-
is an approximation of the mathematical constant
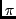 , which equals
the area of a unit circle. This global variable approximates
, which equals
the area of a unit circle. This global variable approximates 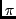 to
24 decimal places.
to
24 decimal places.
- e
-
is an approximation of the mathematical constant e. The primary property
of e is that if y = ex, then
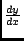 = ex. This global
variable approximates e to 24 decimal places.
= ex. This global
variable approximates e to 24 decimal places.
- argv
-
is a list of the arguments (interpreted as string's)
with which the Glish script
was invoked. Presently the Glish interpreter is invoked with a
filename to interpret followed by a list of arguments.
So, for example, if a script is invoked using:
glish script.g hello, how are you
then argv is a string value with 4 elements, ``hello,",
``how", ``are", and ``you".
- environ
-
is a record providing access to the UNIX environment
(i.e., what in C programs is accessible via
getenv()). Each environment
variable corresponds to a string-valued field in the record.
For example,
environ.HOME
returns the value of the $HOME environment variable. Naturally
this can also be referred to using:
environ["HOME"]
Changing the environ global does not presently affect the
environment in which Glish clients are run (though it may in the future).
- system
-
is an agent record that contains general information about the
environment (not in an ``environment variable'' sense) in which the
Glish script runs. It also generates events corresponding to changes
in the environment.
The predefined fields of system are:
- version
-
gives the version level of the Glish interpreter. Presently this field's
type is string, though it may change to double in the future to
facilitate inequality comparisons like ``system.version >= 2.1".
- is_script_client
-
is true (T) if the Glish script is run as a script client
(§ 7.10, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) and false (F) if not.
) and false (F) if not.
- print.limit
- allows you to limit how much of
Glish
values is output to the screen (see § 5.3.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).
- print.precision
- allows you to specify the number
of significant digits to use in outputting floating point numbers (see
§ 5.3.1, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).
- tk
- contains the Tk version number if the glishtk.g
(see § 11.8, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) client script with the Tk widgets is loaded.
) client script with the Tk widgets is loaded.
- path.include
- path searched by include when attempting
to include a file (see § 4.15, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).
- path.bin.host
- path searched when starting clients on
the machine host.
- output.pager.exec
- the executable to be started to handle
paging of output, e.g. less or more.
- output.pager.limit
- the number of lines where paging begins.
If set to 0, paging is always done; if set to -1, paging is
never done.
- output.log
- place to log input and output.
(See § 9.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
- output.ilog
- place to log input. (See
§ 9.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
- output.olog
- place to log output. (See
§ 9.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
- output.pager.log
- place to log input and output.
(See § 9.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
- pid
- process id of the current Glish
interpreter.
- ppid
- process id of the current Glish
interpreter's parent process.
- limits.max
- contains the maximum values for
Glish's builtin (non-boolean) numeric types.
- limits.min
- contains the minimum values for
Glish's builtin (non-boolean) numeric types.
The events generated by system are:
- connection_lost
-
indicates the loss of the network connection to a remote host. The
value of the event names the remote host. (See § 16.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for
details as to when this event is generated.)
for
details as to when this event is generated.)
- connection_restored
-
indicates the restoration of the network connection to a remote host. The
value of the event names the remote host. See § 16.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for details
as to when this event is generated.
for details
as to when this event is generated.
- daemon_terminated
-
indicates that a remote glishd daemon terminated; normally this
indicates a problem or bug (see § 16.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for details
as to when this event is generated).
for details
as to when this event is generated).
For example, the following checkpoints some local data whenever the
network connection to the ``frontend'' host drops, and rolls
back to the checkpoint when connectivity resumes:
whenever system->connection_lost do
{
if ( $value == "frontend" )
do_local_checkpoint()
}
whenever system->connection_restored do
{
if ( $value == "frontend" )
roll_back_to_checkpoint()
}
- script
-
has one of two possible values. If the Glish
script is run as a
client of another script, then script is an agent record
(§ 7.2.2, page
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) that can be used to receive events sent by the parent
script and send events back to the parent (See § 7.10, page
) that can be used to receive events sent by the parent
script and send events back to the parent (See § 7.10, page ![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for details).
If the Glish script is running independently, then script is
the boolean value F.
for details).
If the Glish script is running independently, then script is
the boolean value F.

 News
News  FAQ
FAQ
 Search
Search
 Home
Home

![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) and false (F) if not.
) and false (F) if not.
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) client script with the Tk widgets is loaded.
) client script with the Tk widgets is loaded.
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
.)
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for
details as to when this event is generated.)
for
details as to when this event is generated.)
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for details
as to when this event is generated.
for details
as to when this event is generated.
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for details
as to when this event is generated).
for details
as to when this event is generated).
![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) that can be used to receive events sent by the parent
script and send events back to the parent (See § 7.10, page
) that can be used to receive events sent by the parent
script and send events back to the parent (See § 7.10, page ![[*]](../../gif/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) for details).
If the Glish script is running independently, then script is
the boolean value F.
for details).
If the Glish script is running independently, then script is
the boolean value F.