
| Version 1.9 Build 1556
|
|



Next: Examples
Up: The Generic Instrument: III Design of Calibration and
Previous: The Design
The classes SkyModel, SkyJones, VisJones, MJones, ACoh, XCorr are base classes from which concrete classes must be derived. For
example, the most useful form of SkyModel is ImageSkyModel
which can be constructed from an image or set of images. Similarly, we
envisage a ComponentSkyModel which implements Sky Brightness
modeling via a set of discrete components such as Gaussians. Note that
the interface to SkyEquation is via images, but that the internal workings
of a SkyModel are not prescribed. Similarly, the two types of Jones
classes, SkyJones and VisJones, interface to the VisEquation via actual
matrices but may be implemented internally in any way desired.
Fourier transforms are implemented by the FTCoh and IFTCoh objects.
None of the matrices is required. For single dish processing, E must
be present to implement summation over a primary beam. We have chosen
a specific number and set of slots to make integration of different
matrices part of the services supplied by the SkyEquationand VisEquation.
The use of SkyModel is subtle and deserves some description.
- Prediction
- The SkyEquation calls the get method of SkyModel to get a set of Images for which it can do a prediction of the
coherences in a VisSet. Note that because of the form of the
measurement equation, Images are required and, in particular, a
collection of e.g. Gaussian components cannot be used
directly. To obtain the predicted coherences, one uses the predict method of SkyEquation.
- Solution
- To solve for a SkyModel, one uses the solve of the
SkyEquation. This calls the solve method
of the SkyModel. This will usually be an iterative procedure that in
turn calls the gradientsChiSquared method of SkyEquation which
accumulates
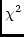 and first and second gradients into the
SkyModel. The gradients are with respect to the set of Images.
Conversion of the gradients to be with respect to the internal
variables of the SkyModel is the responsibility of the particular
SkyModel and is not visible outside of that SkyModel. Thus, for
example, ComponentSkyModel has to take the image form of the
gradient of
and first and second gradients into the
SkyModel. The gradients are with respect to the set of Images.
Conversion of the gradients to be with respect to the internal
variables of the SkyModel is the responsibility of the particular
SkyModel and is not visible outside of that SkyModel. Thus, for
example, ComponentSkyModel has to take the image form of the
gradient of 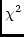 and convert it to be with respect to the
parameters of the various components.
and convert it to be with respect to the
parameters of the various components.
Thus although SkyModel is very general, the interface between the
SkyEquation and SkyModel is quite simple and is based upon Images.
The apply method can apply a correction to an Image.
A similar scheme works for Jones classes. Here the interface is in
terms of the coherence vector.
- Prediction
- The apply method of a Jones class
applies the interferometer gain term (i.e. the direct product of
the Jones Matrices).
- Solution
- The gradients are with respect to these same
matrices. These are accumulated into a Jones classes by the gradientsChiSquared method of the VisEquation. The solve method of the
Jones class is responsible for calling gradientsChiSquared. The
particular Jones class, e.g. PhaseScreenVisJones is
responsible for converting the gradients of
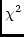 with respect to
the matrices
with respect to
the matrices
 into gradients with respect to the internal
variables of the Jones class e.g. parameters of a phase screen
across a synthesis array.
into gradients with respect to the internal
variables of the Jones class e.g. parameters of a phase screen
across a synthesis array.
- Correction
- The applyInv of a Jones class applies the
inverse of the interferometer gain term (i.e. the direct product of
the Jones Matrices).



Next: Examples
Up: The Generic Instrument: III Design of Calibration and
Previous: The Design
Contents
Please send questions or comments about AIPS++ to aips2-request@nrao.edu.
Copyright © 1995-2000 Associated Universities Inc.,
Washington, D.C.
Return to AIPS++ Home Page
2006-10-15

 News
News  FAQ
FAQ
 Search
Search
 Home
Home
